CB Model¶
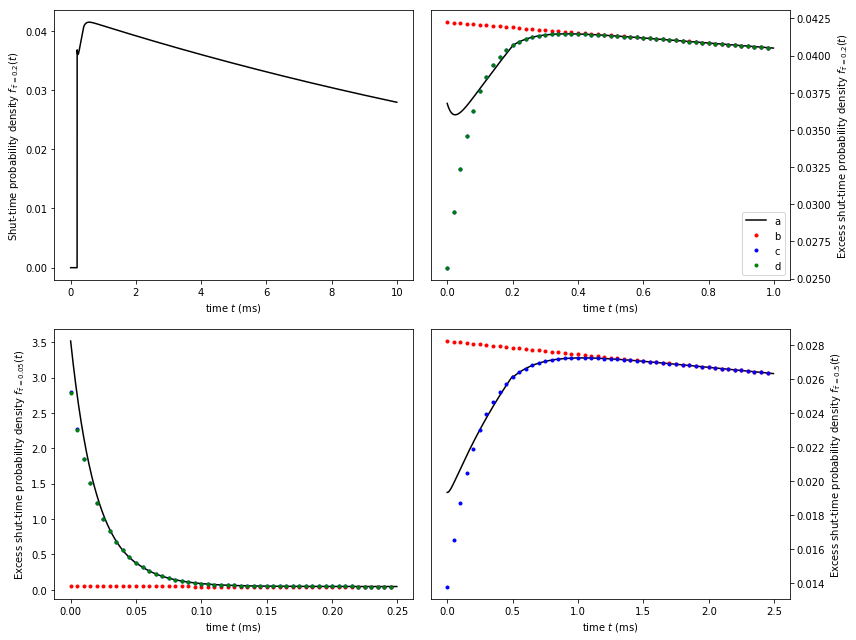
The following tries to reproduce Fig 10 from Hawkes, Jalali, Colquhoun (1992). First we create the \(Q\)-matrix for this particular model from Hawkes, Jalali, Colquhoun (1992). First we create the \(Q\)-matrix for this particular model.
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from dcprogs.likelihood import QMatrix
tau = 0.2
qmatrix = QMatrix([ [-2, 1, 1, 0],
[ 1, -101, 0, 100],
[50, 0, -50, 0],
[ 0, 5.6, 0, -5.6]], 1)
We then create a function to plot each exponential component in the asymptotic expression. An explanation on how to get to these plots can be found in the CH82 notebook.
from dcprogs.likelihood._methods import exponential_pdfs
def plot_exponentials(qmatrix, tau, x0=None, x=None, ax=None, nmax=2, shut=False):
from dcprogs.likelihood import missed_events_pdf
from dcprogs.likelihood._methods import exponential_pdfs
if ax is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1)
if x is None:
x = np.arange(0, 5*tau, tau/10)
if x0 is None:
x0 = x
pdf = missed_events_pdf(qmatrix, tau, nmax=nmax, shut=shut)
graphb = [x0, pdf(x0+tau), '-k']
functions = exponential_pdfs(qmatrix, tau, shut=shut)
plots = ['.r', '.b', '.g']
together = None
for f, p in zip(functions[::-1], plots):
if together is None:
together = f(x+tau)
else:
together = together + f(x+tau)
graphb.extend([x, together, p])
ax.plot(*graphb)
For practical reasons, we plot the excess shut-time probability densities in the graph below. In all other particulars, it should reproduce Fig. 10 from Hawkes, Jalali, Colquhoun (1992)
from dcprogs.likelihood import missed_events_pdf
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2,2, figsize=(12,9))
x = np.arange(0, 10, tau/100)
pdf = missed_events_pdf(qmatrix, 0.2, nmax=2, shut=True)
ax[0,0].plot(x, pdf(x), '-k')
ax[0,0].set_xlabel('time $t$ (ms)')
ax[0,0].set_ylabel('Shut-time probability density $f_{\\bar{\\tau}=0.2}(t)$')
ax[0,1].set_xlabel('time $t$ (ms)')
tau = 0.2
x, x0 = np.arange(0, 5*tau, tau/10.0), np.arange(0, 5*tau, tau/100)
plot_exponentials(qmatrix, tau, shut=True, ax=ax[0,1], x=x, x0=x0)
ax[0,1].set_ylabel('Excess shut-time probability density $f_{{\\bar{{\\tau}}={tau}}}(t)$'.format(tau=tau))
ax[0,1].set_xlabel('time $t$ (ms)')
ax[0,1].yaxis.tick_right()
ax[0,1].yaxis.set_label_position("right")
tau = 0.05
x, x0 = np.arange(0, 5*tau, tau/10.0), np.arange(0, 5*tau, tau/100)
plot_exponentials(qmatrix, tau, shut=True, ax=ax[1,0], x=x, x0=x0)
ax[1,0].set_ylabel('Excess shut-time probability density $f_{{\\bar{{\\tau}}={tau}}}(t)$'.format(tau=tau))
ax[1,0].set_xlabel('time $t$ (ms)')
tau = 0.5
x, x0 = np.arange(0, 5*tau, tau/10.0), np.arange(0, 5*tau, tau/100)
plot_exponentials(qmatrix, tau, shut=True, ax=ax[1,1], x=x, x0=x0)
ax[1,1].set_ylabel('Excess shut-time probability density $f_{{\\bar{{\\tau}}={tau}}}(t)$'.format(tau=tau))
ax[1,1].set_xlabel('time $t$ (ms)')
ax[1,1].yaxis.tick_right()
ax[1,1].yaxis.set_label_position("right")
ax[0,1].legend(['a','b','c','d'], loc='best')
fig.tight_layout()
from dcprogs.likelihood import DeterminantEq, find_root_intervals, find_lower_bound_for_roots
from numpy.linalg import eig
tau = 0.5
determinant = DeterminantEq(qmatrix, tau).transpose()
x = np.arange(-100, -3, 0.1)
matrix = qmatrix.transpose()
qaffa = np.array(np.dot(matrix.af, matrix.fa), dtype=np.float128)
aa = np.array(matrix.aa, dtype=np.float128)
def anaH(s):
from numpy.linalg import det
from numpy import identity, exp
arg0 = 1e0/np.array(-2-s, dtype=np.float128)
arg1 = np.array(-(2+s) * tau, dtype=np.float128)
return qaffa * (exp(arg1) - np.array(1e0, dtype=np.float128)) * arg0 + aa
def anadet(s):
from numpy.linalg import det
from numpy import identity, exp
s = np.array(s, dtype=np.float128)
matrix = s*identity(qaffa.shape[0], dtype=np.float128) - anaH(s)
return matrix[0,0] * matrix[1, 1] * matrix[2, 2] \
+ matrix[1,0] * matrix[2, 1] * matrix[0, 2] \
+ matrix[0,1] * matrix[1, 2] * matrix[2, 0] \
- matrix[2,0] * matrix[1, 1] * matrix[0, 2] \
- matrix[1,0] * matrix[0, 1] * matrix[2, 2] \
- matrix[2,1] * matrix[1, 2] * matrix[0, 0]
x = np.arange(-100, -3, 1e-2)
# For some reason gcc builds with regular doubles have trouble finding the
# roots with alpha=2.0 the default so override it here
print("Lower bound for all roots is {}".format(find_lower_bound_for_roots(determinant, alpha=1.9)))
print(eig(np.array(anaH(-160 ), dtype='float64'))[0])
print(anadet(-104))
Lower bound for all roots is -126.51309385718378
[ 0.00000000e+00 6.57926167e+33 -5.60000000e+00]
0.0